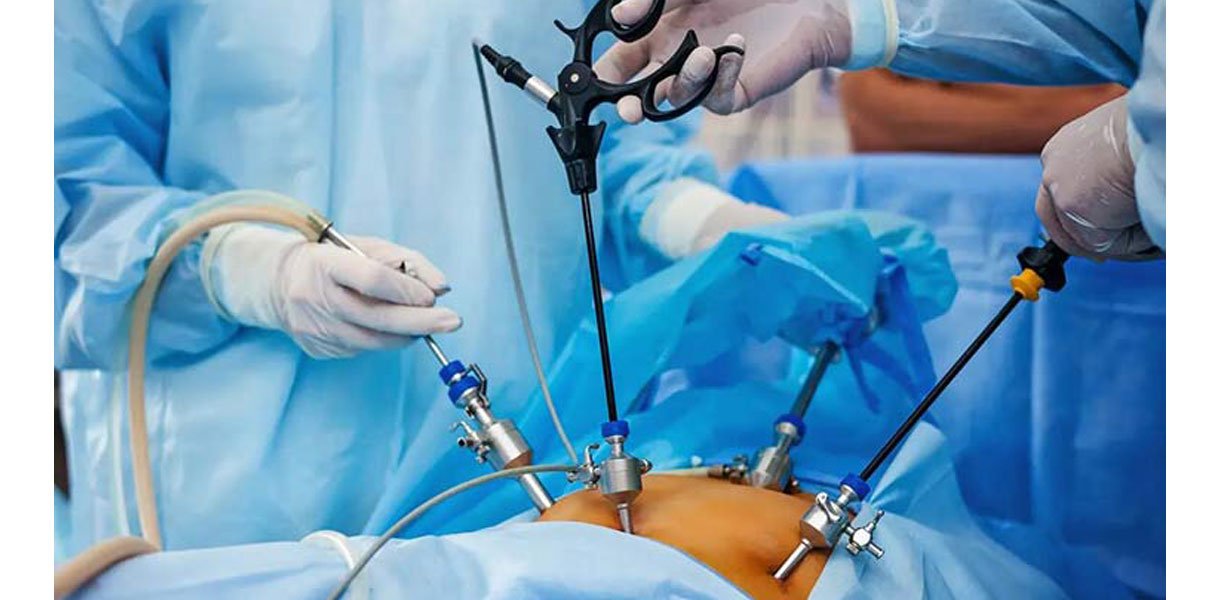
Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a surgical technique performed through small incisions using a laparoscope. A laparoscope is a long, thin tube with a high-intensity light and a high-resolution camera at the front. When inserted into the body, it allows surgeons to view the inside of the abdomen and pelvis on a monitor.
Minimally Invasive: Laparoscopic surgery involves making several small incisions, usually 0.5 to 1.5 cm, compared to a single larger incision in traditional open surgery. This results in less tissue damage and quicker recovery times.
Laparoscope Use: The laparoscope transmits images of the internal organs to a monitor, providing a clear and magnified view for the surgeon. This helps in accurate diagnosis and precise surgical procedures.
Insufflation: The abdomen is often inflated with carbon dioxide gas to create a working space for the surgeon. This allows better visualization and manipulation of the organs.
Laparoscopy is widely used due to its many advantages and is continually evolving with advances in technology and techniques. It is important for patients to discuss the potential risks and benefits with their surgeon to determine if laparoscopic surgery is the best option for their specific condition.